Sustainability of Construction Industry through Green Building Concept and Optimum Utilization Of Resources
Introduction:
Green Building Concept is about optimum utilization of resources, reduction of Green House Gases (GHG) and minimum operational cost. Consumer perception, durability, energy consumption and basic cost are some important factors in the Construction Activities which directly affect the resident. WORLDWIDE, construction, real estate and consumer sector have awakened to the environmentalism boom which is the result of heightened public awareness about climate change and energy efficiency. The tsunami in late 2004, the hurricanes that devastated the US west coast in 2005 and east coast in 2011 and 2012 most recently, the increase in temperature in summer, the melting of ice-bergs have all played a significant role in increasing awareness of this threat. Construction agencies across the world are developing strategies to sustain themselves in the wake of climate change and resource sustainability. This has to follow in India too and thus have to adopt two-pronged approach to combat sustainability.
First by working towards developing a low carbon landscape: Construction industry has to make efforts to optimize the energy efficiency of infrastructure to match with mandatory or TERI norms and voluntary compliance as per ECBC user guide about electric consumption etc. Moving forward with stricter GHG targets, there will be growing demand for new low carbon solutions which must have steps to understand how they modify the existing material resources; products and reposition them to ensure their sustainability in the real estate industry. Construction material manufacturers must also start working on these lines. Cement industry became the first to attain such status to use the waste products like fly ash from power plant and blast furnace slag from Iron Industry etc and thereby bring out Portland Pozzolana Cement or blended cement and thus reducing the carbon footprints and save resources in such product/operation.
Second, by building new low carbon construction setup: In tandem with the efforts mentioned above, there is a move to develop new radically-effective low-carbon generating raw material & thus construction. Builders across the World including India have awakened to this requirement. Green initiatives include green buildings; efficient planning & lighting and air conditioning systems, the use of renewable power such as solar, wind & biomass and promotion of green materials are some of items for use in Green Buildings.
Sustainability:
Sustainability of Global System is a primary issue which will affect the entire Eco System on Earth and influence the Environment along with availability of resources. The sustainability concerns the conducive environment and securing health for citizens as essential requirement which should aim for availability of resources and reducing, re-using, recover or recycling (4R’s) of wastes through their safe, efficient and scientific management. Factors affecting mankind on earth and sustainable development are:
- Global Warming
- Population growth and its Urbanization
- Excessive Waste Generation
- Limited supply of Natural Resources
- Extensive use of Conventional Energy
- Pollution of air, water and soil etc.
The general definition of sustainability of system is meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of further generations to meet their demands. Visualization of sustainability is the realization that today’s population is merely borrowing resources and environmental benefits from future generations. This can also be seen in the context that total Human beings account for only 0.00018% of earth mass, while as they use about 20% of the earth’s resources. Some of these factors are discussed in brief here.
Global Warming:
In 2004, the average worldwide power consumption of the human race was about 15 TW or 15×1012 W with 85% coming from burning fossil fuels like Oil, coal, natural gas etc. The energy consumption in India is also high and it is increasing many fold, say from 4.16 to 16.8 Quadrillion Btu in the last few years, putting India next to most developed countries of World in energy consumption. Because of requirement of thermal power generation and various other human activities, lots of Green House Gases (GHG) are produced. Following are some of the main constituents of Green House Gases, which enter into atmosphere.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Fluorinated Gases etc.
In addition to the these gases, Volatile organic compounds, asbestos, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) and combustion gases also affect air quality. Some of these gases are introduced in the indoor environment also by paints, glues, solvents, wood preservatives, installation of carpets or through cleaning products.
Effect of Global Warming:
Because of climate change, the air is getting warmer; summer comes sooner in most Continents including Europe and America. Sea level is rising & the Maldives Island is sinking. Mangrove forests of Sunderban in India, which are the unique islands and world’s most prosperous group of 104 Rainforest Islands, are likely to be wiped out from earth’s map soon. In fact 16% of Sunderban Islands have already been submerged in the ocean. Now the threat of submerging is looming large on Sagardeep, the 4th biggest of the existing island. It is also on this Island, that the annual Mela of Gangasagar is held. In general, the global warming may result in:
- Erratic sessions giving very hot or very cold climate
- Likely temperature rise
- Sea level rise – likely to rise by 0.28 – 0.43 m
- Arctic summer sea ice reducing or disappearing in a century or earlier.
- An increase in heat waves
- Rise in tropical storm intensity.
- Erratic or Changed climate conditions.
According to NASA satellite data, the Arctic Ocean could be nearly ice free soon, much faster than previous predictions. Faster melting of ice there means eventual sea level rise and more immediate changes in winter weather because of less sea ice. While sea ice reflects about 80% of the sun‘s heat off earth. When there is no sea ice, this 80% of the heat goes directly into the ocean which than warms up everything else. Warmer oceans ultimately lead to more ice melting. The glaciers feeding water for the Holy River GANGA at Goumukh are also melting faster than it should. It means the river GANGA could become a stream in another 100 years or so. This would leave more than 50 million people hungry and thirsty who are living and surviving on the banks of river Ganga all along its alignment / route.
Population Growth And Urbanization:
In 1950, New York and few others were the only cities in the world with a population of more than 10 million. The number of cities with a population of more than 10 million increased to 5 in 1975 and above 20 in 2001. It is expected that this will increase to 25 or more cities by the year 2015. Currently, about one third of the worlds’ population lives in urban areas. By 2030, urban dwellers will make up roughly 60% of world’s population. The percentage of urban population in India was about 27.8% in 2001. It is projected that in Asia and Africa there will be more urban dwellers than any other continent of the World and Asia will comprise 54% of world’s urban population by 2030. In India the urban population may increase to 40% or so by 2015. Thus, a News Item: New Delhi, April 23 –
By 2030, Indian towns may turn dry, stinking hellholes, Dry taps, untreated sewage and piles of solid waste strewn all around.
The report of McKinsey & Company predicts that such phenomenon may become a stark reality of our urban landscape by 2030, when India’s urban population will grow. The problem is much bigger, as less than 38 percent of the population, 350 million people, in these cities may have access to sanitation facilities and 78 percent to clean drinking water. “India’s approach to urbanisation is likely to result in urban gridlock and chaos, jeopardising the present growth rate. Thus, we need to act urgently for well being of its citizens and economy”. Population growth coupled with urbanization results in significant impacts on the environment and many other related problems like:
- Deforestation.
- Increased Ambient Temperature & Changed Weather Pattern
- Reduction in Farm Land and Subsequent Food Shortage.
- Decreased Air Quality
- Increased Water Runoff and decreased water Quantity & Quality.
- Loss of Aesthetic Beauty/Character of the Community places.
Deforestation is closely linked with negative environmental consequences such as loss of bio diversity, Global warming, Soil erosion and desertification. This also lowers water table and flood volume increases. Deforestation also affects rain forest survival.
Excessive Waste Generation:
Huge amount of waste is generated every day in each Indian city and even rural areas. For example Delhi alone generates about 650 tons of Garbage every day. By 2020 its amount may reach 1,800 tons. In the cities, the solid waste disposal areas are outside city which are miles away. Such amount of waste disposal is a Herculean task and needs space for dumping and fuel for transportation upto disposal areas. The central pollution Control Board estimates the current quantum of municipal solid waste generation in India to the tune of 50 million tons per annum. Waste generation in major Indian cities generally range from 0.5 to 0.8 kg per day per person.
 In addition, the hazardous waste generation is around 4.4 million tones. A typical solid waste dump is shown in figure 1. Construction industry also produces huge waste called demolition waste or MALWA. The waste also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions apart from nuisance and occupying space. The waste prevention and/or its recycling will reduce greenhouse gases and methane gas emissions etc.
In addition, the hazardous waste generation is around 4.4 million tones. A typical solid waste dump is shown in figure 1. Construction industry also produces huge waste called demolition waste or MALWA. The waste also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions apart from nuisance and occupying space. The waste prevention and/or its recycling will reduce greenhouse gases and methane gas emissions etc.
Similarly nearly 90 per cent of the liquid sewage which is about 40,000 million liter; generated daily by cities that flow into streams, rivers and sea doesn’t met environment norms. Waste water should generally be of bathing quality to meet the standard of waste water disposal being dumped into rivers by cities. In cities, where about 36 percent of the country’s people live, is polluting over 70 percent of the water sources, says a report released by the Central Pollution control Board. Further, 60-70 per cent of the sewage generated in the country may go untreated. The report states that if existing services are not improved drastically, the per capita water supply to an average citizen could drop drastically from an average of 105 litres to only 50-60 litres or less a day in the next few years.
Waste Management:
Solid waste reduction and/or its recycling will help improve global climate change. The waste contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and thus waste prevention and/or its recycling will reduce greenhouse gases and methane gas emissions etc. Waste management will involve different methods for its processing. Waste management is on the principle of 4R’s; i.e. Reduce, Recycle, Recover and Reuse. Waste Management is generally Collection, Transport, Processing and Recycling or Disposal of resultant materials. It involves solid, liquid or gaseous substances to recover or dispose them. A typical waste product distribution in any solid waste dump in Indian cities (as analyzed) at any one time at a particular place is given in figure 2.
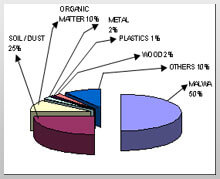
Waste management will involve different methods for its processing. Waste management is on the principle of 4R’s; i.e. Reduce, Recycle, Recover and Reuse. Waste Management is generally Collection, Transport, Processing and Recycling or Disposal of resultant materials. It involves solid, liquid or gaseous substances to recover or dispose them. A typical waste product distribution in any solid waste dump in Indian cities (as analyzed) at any one time at a particular place is given in figure 2.
Creative ways have been found to reduce and better manage Municipal Solid Waste (MSW). This includes reduction at source, recycling (including composting) and disposal. The most environmentally sound management of Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) is achieved when these approaches are put into practice of waste management in order to have sustainability. Out of all approaches, recycling is most relevant as it will also conserve the resources. A typical method or steps for recycling the waste is given here.
Recycling the Waste:
The present development scenario is quite different from earlier times due to diverse factors such as complex user needs, enhanced level of comfort and many technological advances. Yet it is possible to work within the constraints and find meaningful design solutions which can still use less energy & create less waste or facilitate recycling during operation. Various steps in this direction are given below.
Step 1: Collection: Waste or recyclables differ from region to region and from time to time, however, Ist step in this direction is to collect the waste combined or segregated by various possible methods as given below:
1) Municipal collectors,
2) Drop-off centers,
3) Buy-back centers
4) Deposit/refund programs
Step 2: Sorting / Processing: The next stage is to send it to recovery centers to be sorted out & wash/clean and prepare for manufacturing / processing for different commodities.
Step 3: Manufacturing: Once separated and cleaned, the recyclables are ready to undergo the third phase of processing loop. Many products can be manufactured with total or partial recycled content. Demolition waste can be used in making aggregate for fresh concrete or used in Highway Construction etc. Recycled plastic materials are also used in applications such as manufacture of cheep utility items like benches, flower pots, asphalt pavement, perforated blocks etc.
Utilization of Demolition Waste (MALWA) in Construction Industry:
The concrete construction happens to be the most sustainable technique in the developing countries. While it is a blessing that concrete is also an environment friendly product whose increased production generates less pollution and more employment. Though, their ingredient like OPC cement is harmful to ecology, which warrants its lesser consumption for green house gases and sustainable development. While designing a building and minimize its environmental impact, it is important to look at the complete life cycle effect of the building industry including material acquisition, manufacturing, construction, operation, and in the process using optimum quantity of cement and recycled materials.
Coarse Aggregate: Normally coarse Aggregate is the fractured stone from rocks in hills or pebbles from river bed, and because of shortage / depletion of the supply of good conventional aggregate in certain regions, the need for development of recycled aggregate technology is important. It is similar to fly ash, which is an Industrial waste material. Fly ash is chemically reactive when, mixed with cement for use in cement or concrete. This is useful as a partial substitute of cement, as it gives better concrete and having better impermeability record. Similarly recycling of demolished waste will offer, not only the solution of growing waste disposal problem and huge energy requirement, but will also help construction Industry in getting aggregates for full or partial replacement of conventional aggregate.
The demolition waste can be converted to Course aggregate after light crushing and sieving. After sieving, fines left out can be used as filler material for plinth or highway embankment or can go back to river bed from where river sand is coming. Then make concrete with such aggregate after mixing cement and other ingredients as per concrete mix design. Since the waste is being generated all over the country so it should be managed locally or recycled (recycling unit should be tailor made to that area and a portable unit) and used in construction industry there itself. This type of processing the waste will make the system Sustainable. The demolition waste aggregate after processing can be used in many such applications given below.
- Low grade fresh concrete for use in building construction.
- Use of such concrete for making similar to conventional type bricks and using them in place of burnt clay bricks.
- Highway Construction for embankment filling, casting curve, chute drain, median drain & side drain components.
- Recycled materials are also used in plinth and embankment filling.
- Making park benches and pedestrian paths etc.
The demolition waste can be collected locally from buildings being renovated. The foreign matter is sorted out and broken into the pieces of approximately 20 & 10 mm size with the help of light crusher. Then such material is mechanically sieved through IS sieve of 26.5 mm & 12.5 mm and than 4.75 mm to remove higher & finer particles and separate in 20 and 10mm size aggregate. The higher than 26.5 mm size is broken again and finer particles passing through 4.75 mm can go back to river bed in the same trucks which bring sand from river. Typical look and shape of this aggregate is shown in figure 3.
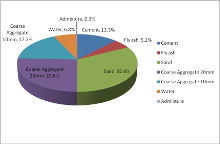
Construction Industry: Construction industry can use the Building Demolition waste (MALWA) easily. Generally the requirement of aggregate in a concrete is about 45% as shown in figure 4. Few typical applications of such concrete with the use of recycled aggregate in construction are given here.
a) Manufacturing the Building Blocks/Bricks out of Demolition Waste:
Recovering course aggregate from Demolition waste after light crushing & sieving can be used to cast bricks/blocks to be used in construction of walls in place of burnt clay bricks. Make concrete mix with nominal amount of cement say 150 Kg per cum of concrete and other ingredients and then cast in the form of conventional type of bricks of size 230x115x70 mm or similar. It can also be casted in appropriate size of blocks/cubes as per the conventional method. They can be cured in open with water sprayed a few times in the day. Shape of such typical bricks is shown in figure 5.
- Figure 4 – Distribution of Ingredients in a typical Concrete Mix
- Figure 5 – Typical Solid or Hollow Concrete Blocks made with demolition waste aggregate
Use and Performance:
They can be beneficially used in conventional wall construction of buildings as shown in figure 6 and/or for building foundation and road shoulder construction etc. Such concrete bricks attain good compressive strength which is comparable or higher to Ist quality brunt clay bricks. It is seen that strength and density of such bricks is more when recycled aggregate is used. These bricks are superior to brunt clay bricks so they perform very well and are more desirable to conventional bricks.
- Advantages of Using Waste Concrete in Bricks/Blocks:
- By making use of locally available demolition waste aggregates, there would be sufficient reduction in aggregate requirement at construction site.
- It would help in improving the local economy rather than spending for procuring burnt bricks from distant places
CO2 emission is almost nil in this process. - Top soil of earth will be saved which is used in making burnt clay bricks and thus environmentally viable.
- When such bricks are used in walls, they give more durable construction and many times one can save the material and cost involved in plaster.
b) Use in General Purpose Concrete:
Concrete made with recycled aggregate can also be used for various applications in building such as for foundations, beams, slabs etc. A concrete mix with recycled aggregate was designed in the grade of M 25 was designed by author with cement content of about 300 Kg/cum or as required. Few simple applications like flower pots, cattle feed pan cast with such concrete is shown in figure 7.
- Figure 7 – Some General Purpose Items made with concrete using Recycled Aggregate
- Figure 7 – Some General Purpose Items made with concrete using Recycled Aggregate
c) Use Of Demolition Waste Aggregate In Highway Construction:
Highways are the biggest user of aggregate during construction. Such recycled aggregate can also be used in Highway construction. With the concept of its use in making bricks, the recycled aggregate concrete can be used for casting curve, chute drain, median drain & side drain components of Highways. These components can be pre-cast with such concrete mix. This concrete can also be used for the following components:
- Dry Lean Concrete (DLC).
- Embankment filling
- Casting embankment drainage components etc.
Green Buildings and Sustainability of Resources:
Considers reuse/recycling as new options once the building has reached the end of its service life. Its successful integration with the virgin material in construction enhances the industry and availability of raw material. It also helps construction industry and minimizes the dumping of waste on road in and around the city. The recycling properties of such concrete are also good. Concrete waste in crushed form can also be effectively used as aggregate in making fresh concrete and for making concrete blocks/bricks similar to brunt clay bricks. Recycling of concrete waste along with construction demolition waste will conserve resources and save landfill space.
Further, the use of manufactured sand and mining waste in place of river sand is also environment friendly and can be used in concrete. Several other byproducts like foundry sand, broken glass; fly ash etc can be equally beneficial in concrete as replacement of sand and will make the construction sustainable.
The consumer’s response to changing materials is of great importance and efforts must be made for convincing the public. In such a price-sensitive market, operational cost of buildings are also of prime importance. Green construction is all about optimum utilization of resources and reduction of operational costs, while reducing the adverse environment impact. It is generally calculated that in green Construction the operational cost can be reduced as much as 20% or more. A recent survey conducted revealed that the vast majority of respondents from developing countries believed in the threat emanating from global warming. It also revealed that a large number of users/consumers in developing countries can even pay more for green buildings. The survey highlights the possible cost benefits accruing from green initiative from which successful and sustainable construction model can be developed by builders. There is promising opportunity for new builders and material manufactures in India who can set up optimized green supply chains for construction material. In addition, such green construction/products for buildings would reduce the impact of their products on the environments. The marginal initial investment required for green buildings normally has a payback period of four to six years during its use.
Apart from operational cost saving in the long term, Buildings/Structures will also get an additional advantage ie. Builders can make green corporate image among users. This could help builders attract and retain new buyers and build resident loyalty. The bureau of Energy Efficiency in India has categorized that the construction sector must be an Energy-intensive industry. The Government of India’s national action plan on climate change, aims to boost energy efficiency and put stricter regulation to reduce the demand for Energy. Moving ahead of these regulations may not only help users but also builders to generate substantial benefit accruing from such construction? With the current economic situation, more and more construction material manufacturers and builders have realized the sustainability as the new mantra. Greening the construction chains and reduce environmental foot print of the building results in lower operational cost.
Green Buildings and Sustainability of Resources:
Considers reuse/recycling as new options once the building has reached the end of its service life. Its successful integration with the virgin material in construction enhances the industry and availability of raw material. It also helps construction industry and minimizes the dumping of waste on road in and around the city. The recycling properties of such concrete are also good. Concrete waste in crushed form can also be effectively used as aggregate in making fresh concrete and for making concrete blocks/bricks similar to brunt clay bricks. Recycling of concrete waste along with construction demolition waste will conserve resources and save landfill space.
Further, the use of manufactured sand and mining waste in place of river sand is also environment friendly and can be used in concrete. Several other byproducts like foundry sand, broken glass; fly ash etc can be equally beneficial in concrete as replacement of sand and will make the construction sustainable.
The consumer’s response to changing materials is of great importance and efforts must be made for convincing the public. In such a price-sensitive market, operational cost of buildings are also of prime importance. Green construction is all about optimum utilization of resources and reduction of operational costs, while reducing the adverse environment impact. It is generally calculated that in green Construction the operational cost can be reduced as much as 20% or more. A recent survey conducted revealed that the vast majority of respondents from developing countries believed in the threat emanating from global warming. It also revealed that a large number of users/consumers in developing countries can even pay more for green buildings. The survey highlights the possible cost benefits accruing from green initiative from which successful and sustainable construction model can be developed by builders. There is promising opportunity for new builders and material manufactures in India who can set up optimized green supply chains for construction material. In addition, such green construction/products for buildings would reduce the impact of their products on the environments. The marginal initial investment required for green buildings normally has a payback period of four to six years during its use.
Apart from operational cost saving in the long term, Buildings/Structures will also get an additional advantage ie. Builders can make green corporate image among users. This could help builders attract and retain new buyers and build resident loyalty. The bureau of Energy Efficiency in India has categorized that the construction sector must be an Energy-intensive industry. The Government of India’s national action plan on climate change, aims to boost energy efficiency and put stricter regulation to reduce the demand for Energy. Moving ahead of these regulations may not only help users but also builders to generate substantial benefit accruing from such construction? With the current economic situation, more and more construction material manufacturers and builders have realized the sustainability as the new mantra. Greening the construction chains and reduce environmental foot print of the building results in lower operational cost.
Poverty Alleviation through Waste Recycling Concept:
The technologies and the materials used for development should complement to the availability of resources. If such technologies are developed, then the poverty alleviation in the developing countries can be effectively achieved by conservation of energy and reprocessing of waste. The energy and resources saved can be ploughed back for further development which creates a larger employment opportunity.
Processing of Waste should be taken up at a large scale and locally in each of the 5,000 odd cities and towns of the Country. This can generate huge manpower requirement in collecting, transporting, sorting, processing and ultimately using it for replacement of resources in proper shape.
In the rigid pavement concrete where after concreting and edge cutting is done, some concrete is removed and thrown as waste. As the country is having large population below property line and they also need shelter. So they collect even a small bit of usable construction material from anywhere. Author observed during the Highway Construction project that the poor people line up along the construction site (as shown in figures 8) who are eager to collect a handful of waste concrete, when the highway concreting process is going on.
The technologies and the materials used for development should complement to the availability of resources. If such technologies are developed, then the poverty alleviation in the developing countries can be effectively achieved by conservation of energy and reprocessing of waste. The energy and resources saved can be ploughed back for further development which creates a larger employment opportunity.
Processing of Waste should be taken up at a large scale and locally in each of the 5,000 odd cities and towns of the Country. This can generate huge manpower requirement in collecting, transporting, sorting, processing and ultimately using it for replacement of resources in proper shape.
In the rigid pavement concrete where after concreting and edge cutting is done, some concrete is removed and thrown as waste. As the country is having large population below property line and they also need shelter. So they collect even a small bit of usable construction material from anywhere. Author observed during the Highway Construction project that the poor people line up along the construction site (as shown in figures 8) who are eager to collect a handful of waste concrete, when the highway concreting process is going on.
c) Use Of Demolition Waste Aggregate In Highway Construction:
Highways are the biggest user of aggregate during construction. Such recycled aggregate can also be used in Highway construction. With the concept of its use in making bricks, the recycled aggregate concrete can be used for casting curve, chute drain, median drain & side drain components of Highways. These components can be pre-cast with such concrete mix. This concrete can also be used for the following components:
1. Dry Lean Concrete (DLC).
2. Embankment filling
3. Casting embankment drainage components etc.
It can be a blessing for the fast developing country like India that the measures called for sustainable development can also be the measures of poverty alleviation as illustrated in this observation. The reprocessing of waste will further strengthen cause of sustainable development.
Advantages Of Using Demolition waste in Construction Industry:
With the use of recycled aggregates in concrete, the following conclusions and advantages can be drawn.
1. Disposal of Demolition waste / Garbage becomes easier.
2. CO2 emission is almost nil in this process and thus no GHG.
3. Demolition waste (MALWA) aggregate can be used in concrete upto the conventional grades cement concrete in foundation, Retaining walls, Panel walls, slab etc.
4. We can make bricks/blocks, like burnt clay bricks out of this type of concrete. By making bricks from such concrete, the manufacture of conventional clay bricks can be reduced & hence top Soil of earth, which is suitable for agriculture, can be conserved.
5. Highways are the biggest user of aggregates. There it can be used in dry lean concrete (DLC) and concrete paving blocks, drains etc.
6. Finer material after crushing of demolition waste and passing through 2.36 or 4.75 mm IS sieve can be used in embankment or plinth filling or it can go back to river beds in the same trucks which bring sand from river bed.
7. As it can be used as aggregate so it will save the natural resources like Hillocks, River Pebbles etc from extinction and hence environment can be preserved. Resulting floods and droughts will be minimized. Indirect Deforestation of hilly areas will be less.
8. It can keep the roads and streets clean by not dumping demolition waste (MALWA) on the road side. This will also minimize the accidents on roads because of fewer obstructions.
9. It can generate work for unemployed people like collecting demolition waste (MALWA) by Rag pickers etc, and deposit it at Ready Mixed Concrete Batching Plants or similar places for processing etc.
10. Concrete can be readily recycled and reused as base materials for roads, sidewalks and concrete slabs, sparing the use of virgin materials.
11. Using decorative concrete limits finishing materials and harmful VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) and provides a high quality, durable, low maintained surface.
12. Pervious Concrete allows rainwater to naturally filter through it, preventing deposits of oil, grease and other contaminants from entering storm drains and going directly into water supply. This technology is recognized by many countries as a best practice for storm water management.
What Is To Be Done?
It is essential to have an effective sustainable building policy that can deliver economic efficiency by using simple, standardized and good performance materials in all phases of building design, construction and operation. Thus, to have Sustainable Building construction concept, some or all of the following steps can be taken up.
- Authorities / Government should make basic norms – like demolition waste recycling compulsory for all type of constructions in each of 5,000 or odd cities, towns and urban agglomerations in India.
- For enforcing the use of demolition waste (MALWA) in Construction Industry; Guidelines, Specifications and Codal provisions be formulated.
- As concrete is a costly material for poor people but they need it for their small constructions, so some concrete design charts be made with
- Recycled aggregate in concrete which will make it easier to make it for common person.
- Municipalities must make a norm that dumping of demolition waste is not done on road sides.